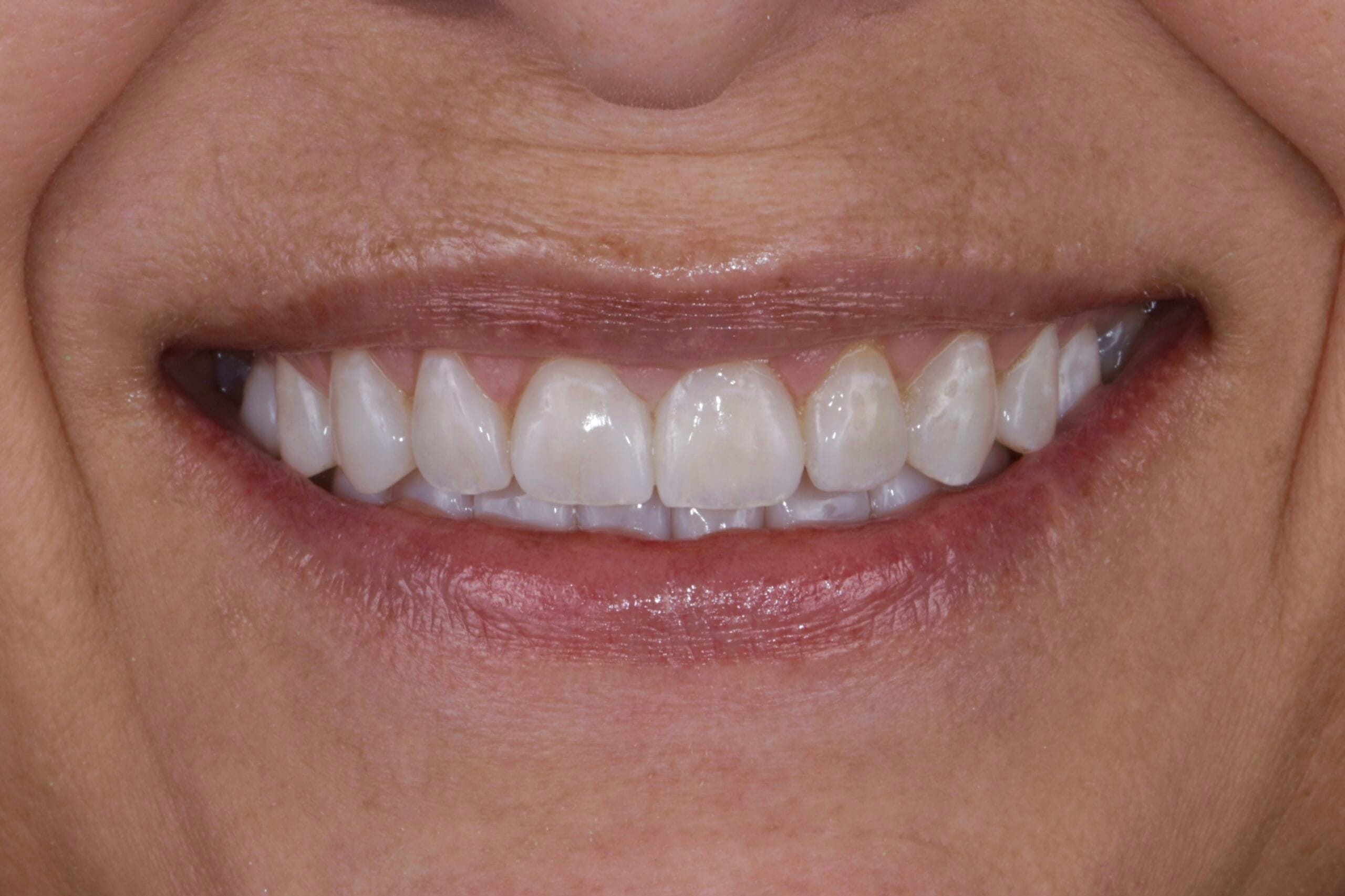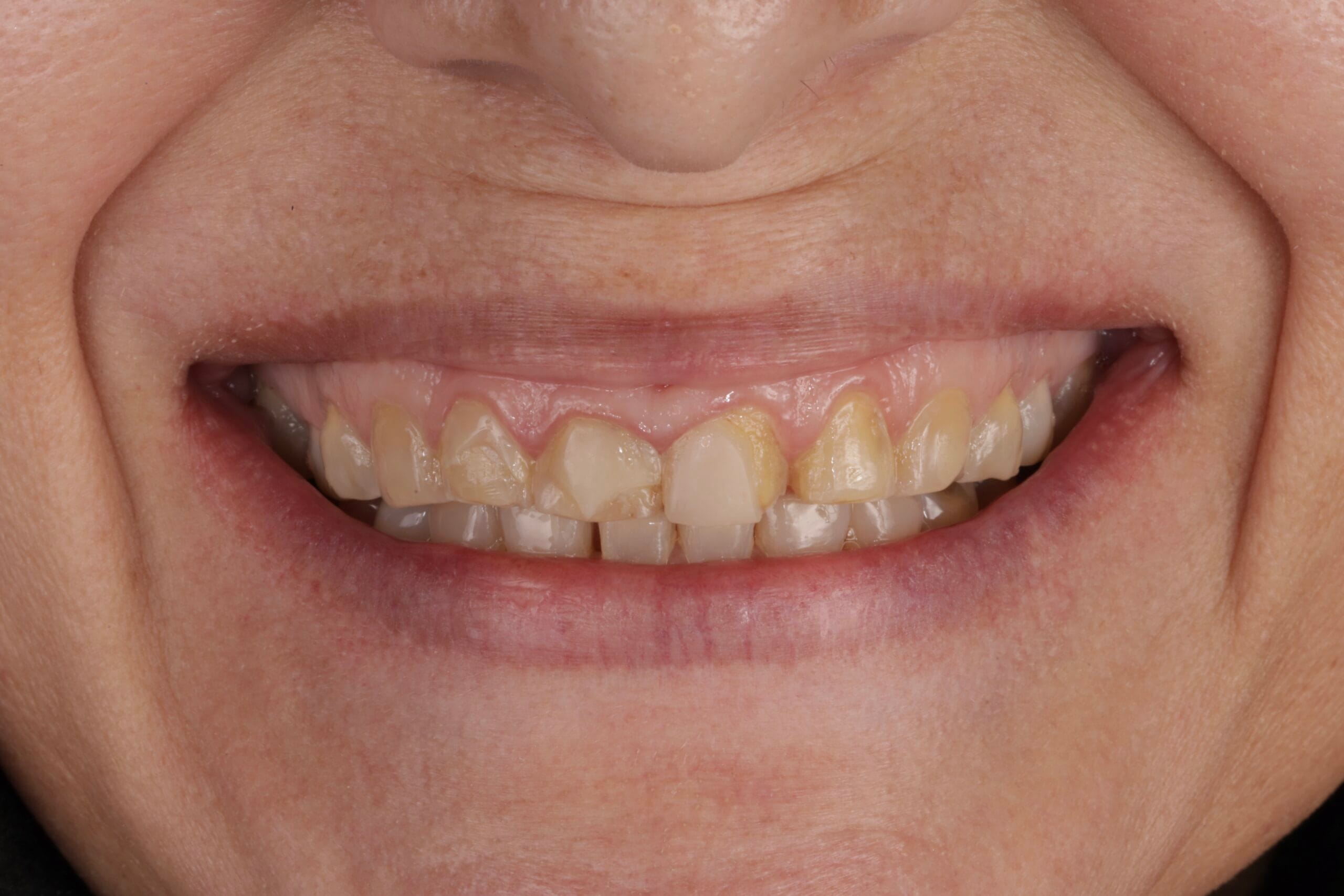
Patient 53 years old, Caucasian, female. She came for dental consultation due to severe wear in her teeth. The different types of materials were explained to her and the patient opted for composite veneers, indirect technique. During the anamnesis the patient denied any pathological or pharmacological history, habits, The patient claims to be a frequent coffee drinker.

On clinical examination, we observed fractured composite veneers dental organs 11,12,21,23, multiple silver restorations in the upper and lower posterior teeth, generalized attrition, class I bite (Figure 2, 3,4).
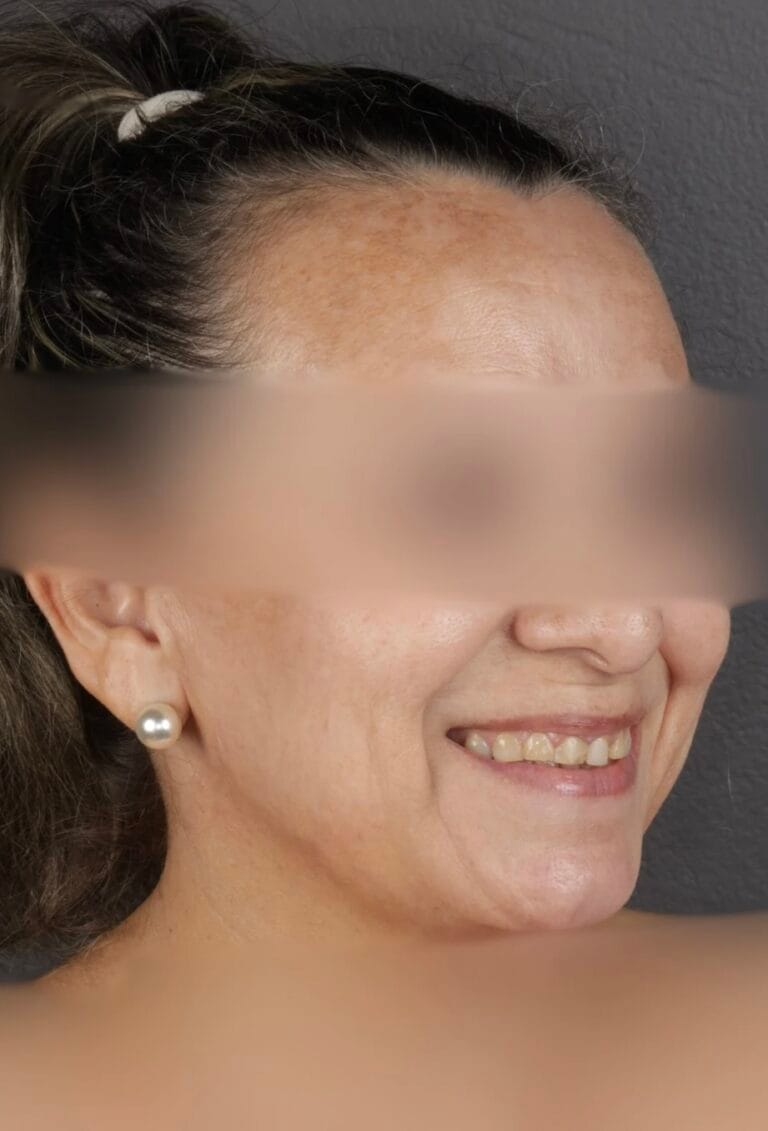
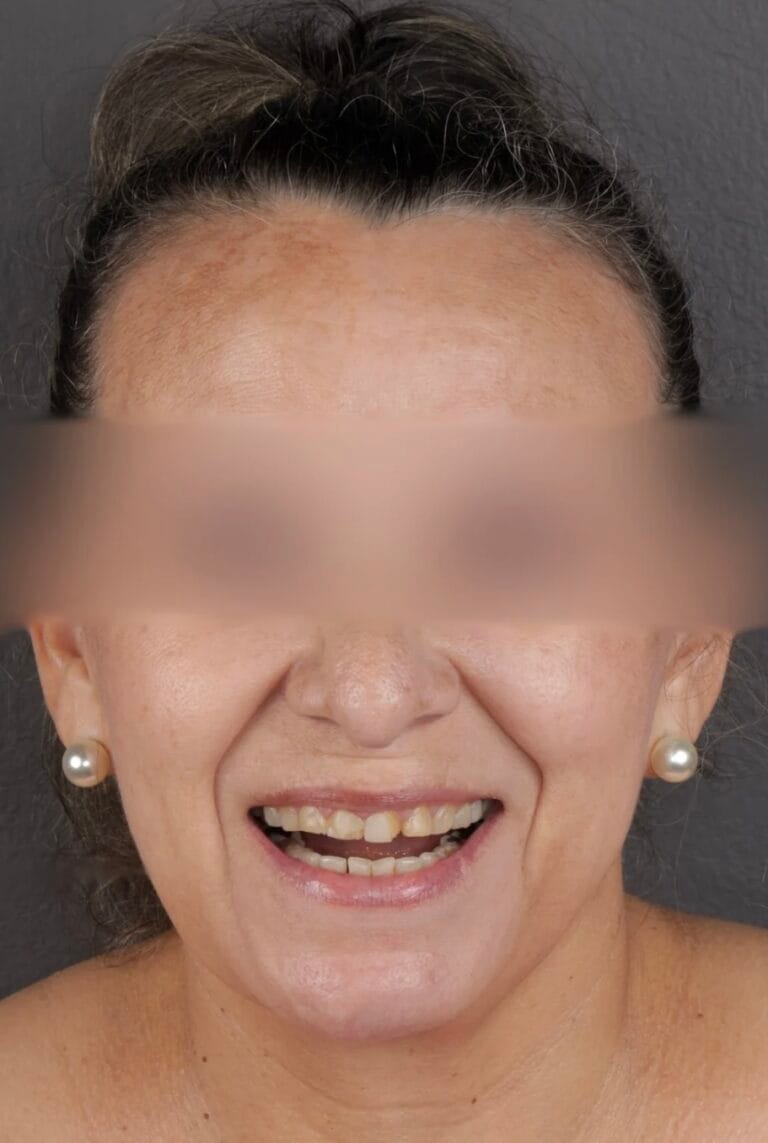

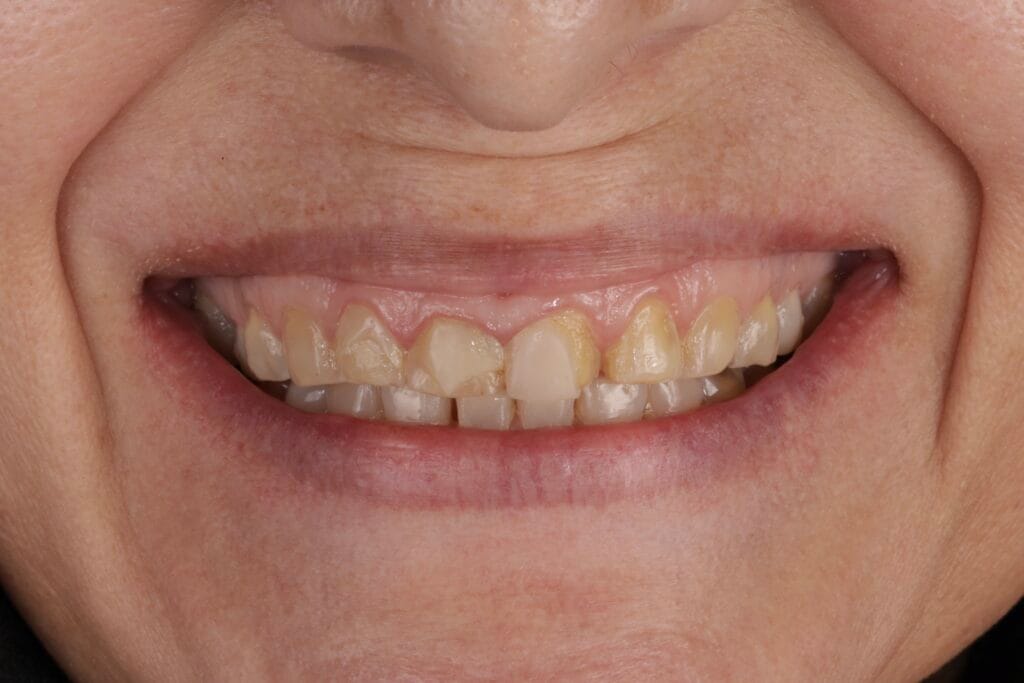
Figure 3. Extraoral photos
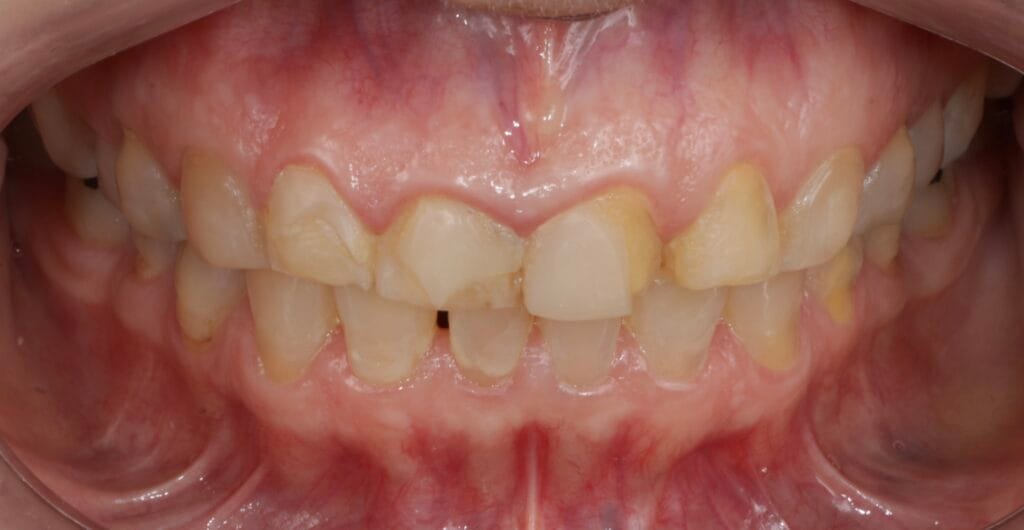
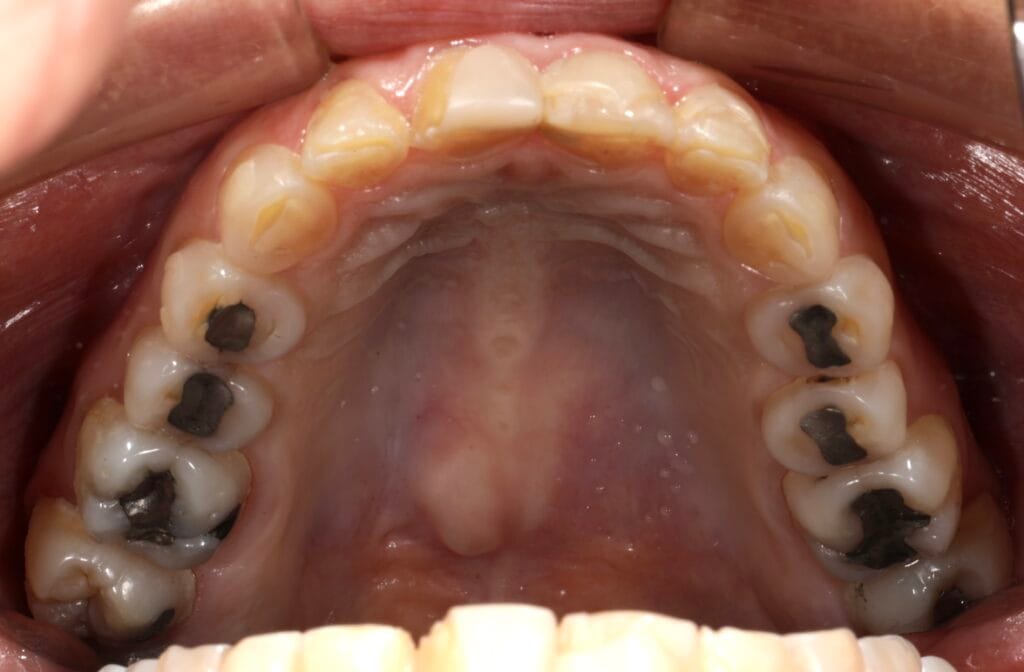
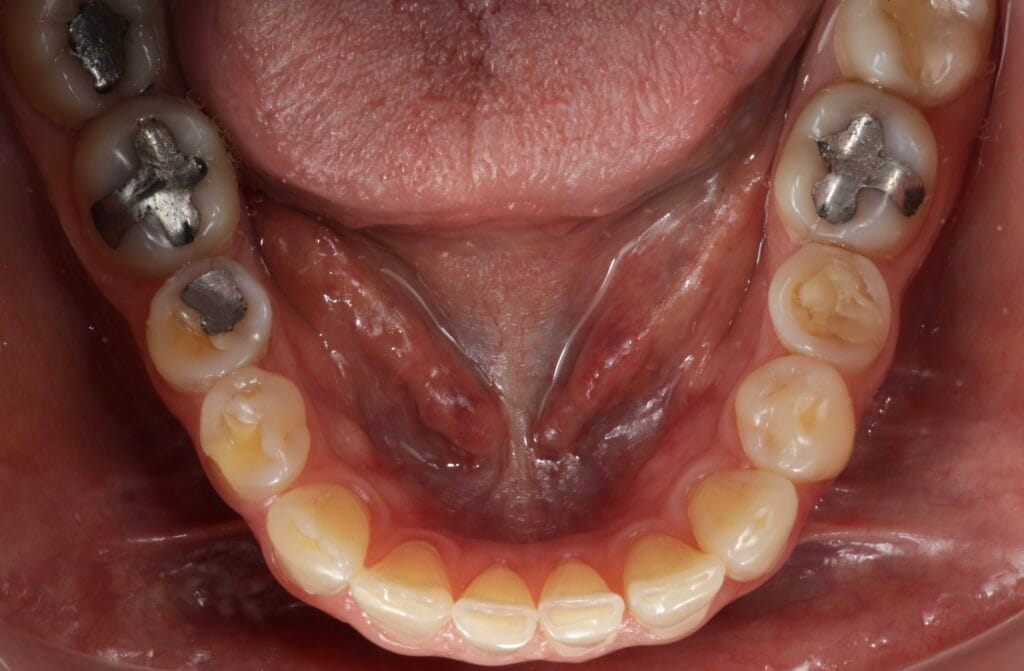
Figura 4. Intraoral Photos
The treatment plan was divided through phases:
– Phase 1: We take extraoral and intraoral photos, take preliminary impressions for case planning.
– Phase 2: Mock-up tria with Protemp, color A1, 3M brand, where the patient approved the shape and size of the teeth. For the color; the patient chose color W BODY 3M, translucent effect on the incisal edge and simulation of white gears on the vestibular surface.
– Phase 3: Removal of composite restorations in vestibular surface, then dental preparation of 20 veneers and 16 table tops in posterior with a 2134F red diamond halo conical bur and definitive impressions in addition silicone and bite registration with gray wax.
RESULTS
– Phase 4: we start with the posterior part to recover the vertical dimension, then we did the dry and wet test of table tops to observe adaptation, presence of premature contacts and color testing.
Subsequently, we performed the tests of the veneers with glycerin, waited for five minutes to hydrate them and we showed to the patient in natural light, how her smile and teeth would look like.
We prepared the veneers and table tops as well as the tooth surface and proceeded to the individual cementation of each one.
First, we cement the table tops and then the dental veneers, using Choice 2 Bisco translucent color.
We remove excess cement, palatal seal, occlusal adjustment and gave to the pacient an activated night guard for bruxism.
Figure 5. Final Result
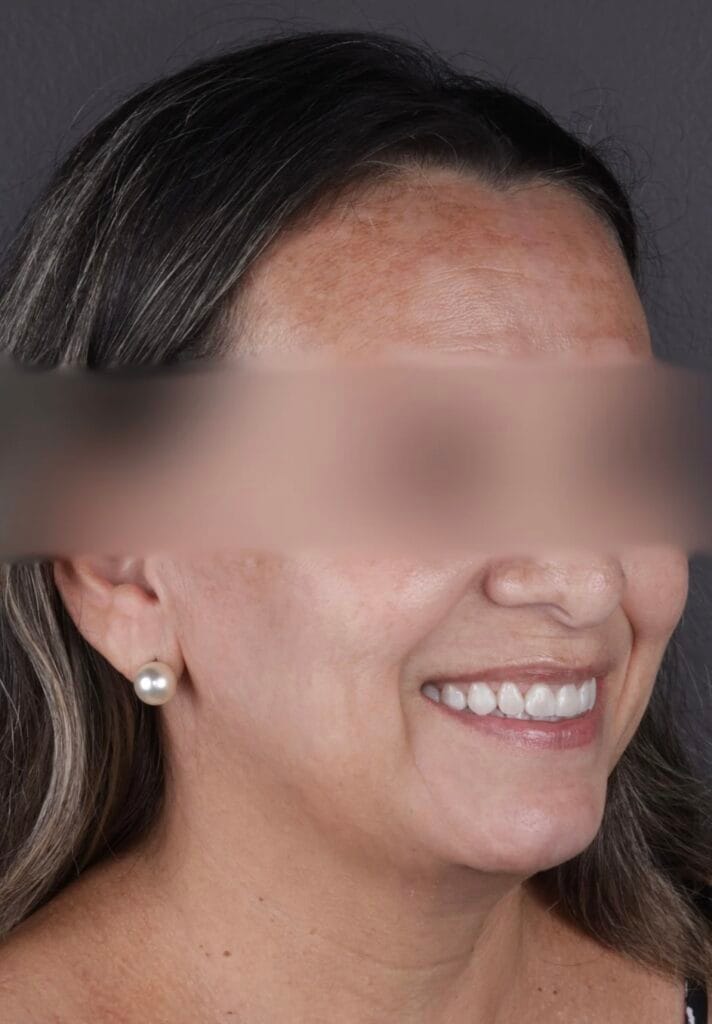
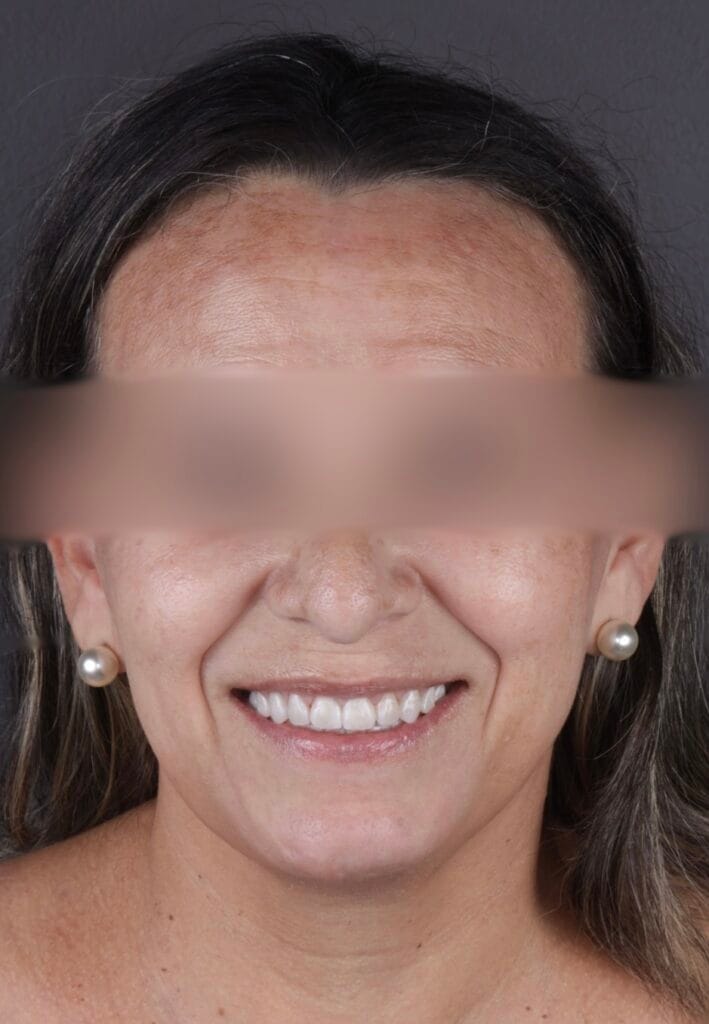

Figure 6. Extraoral Photos (After)
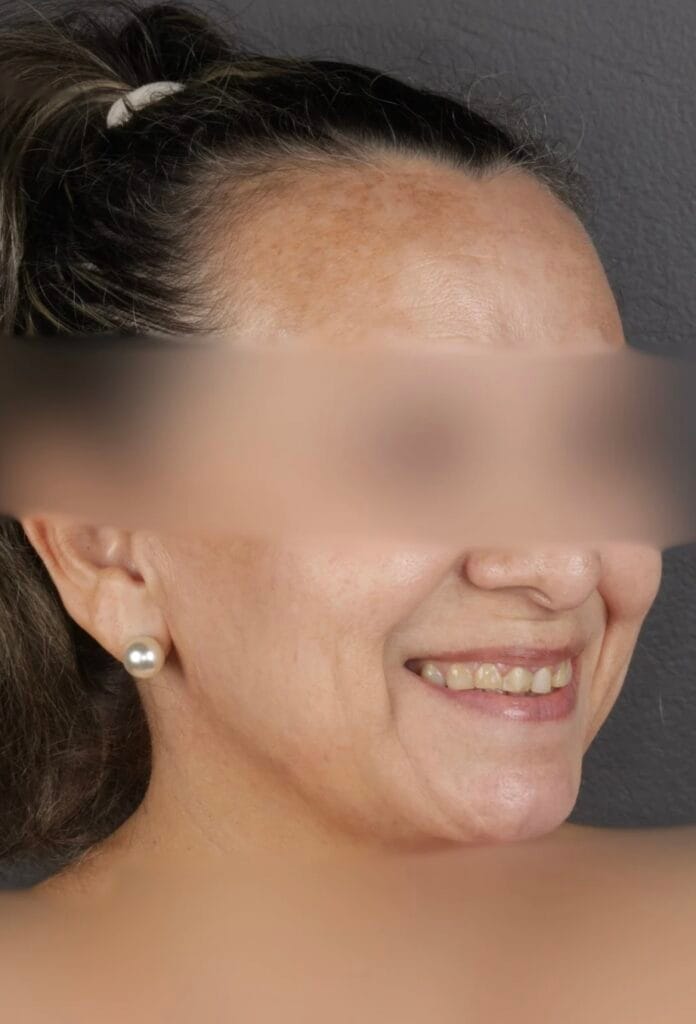

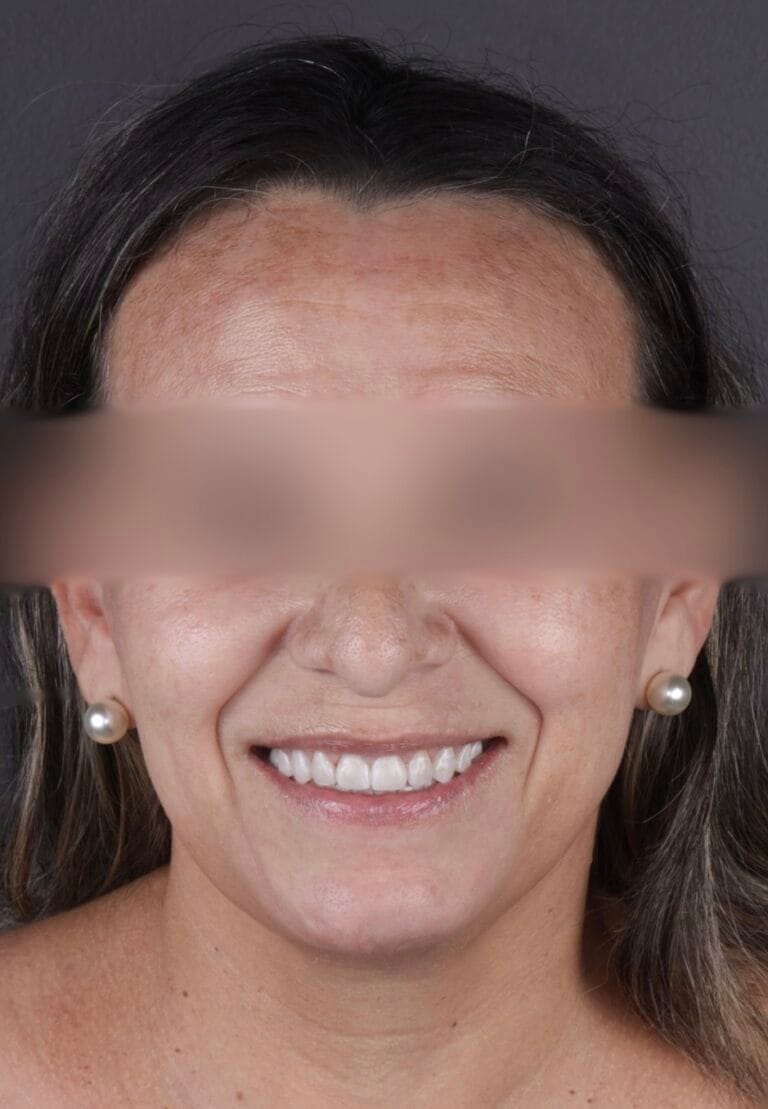


Figura 6 – Extraoral before and after photos
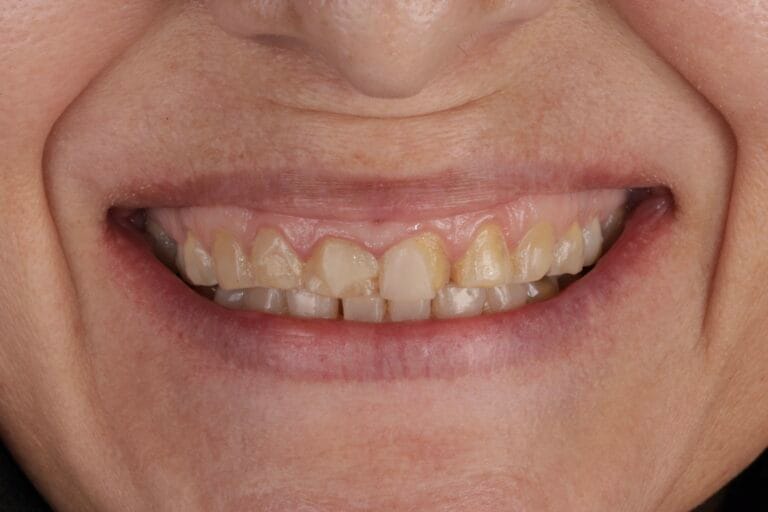
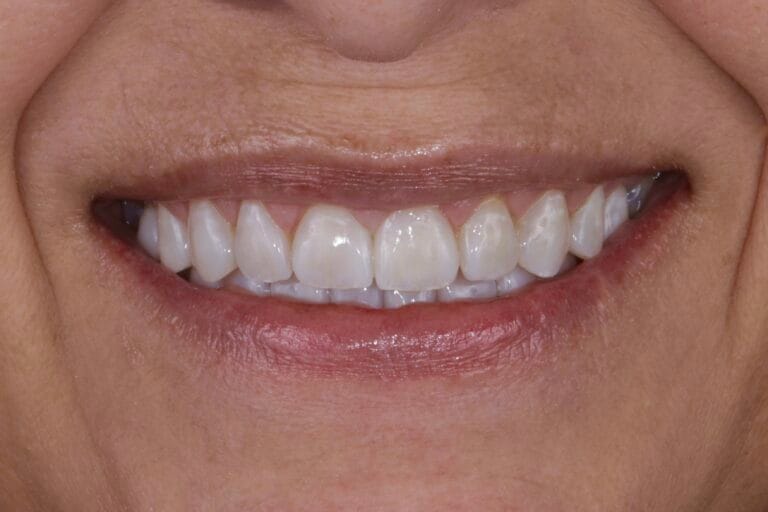
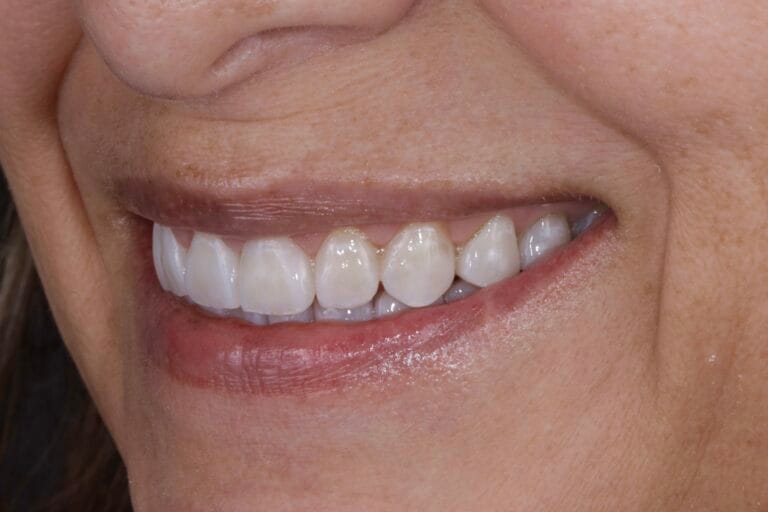
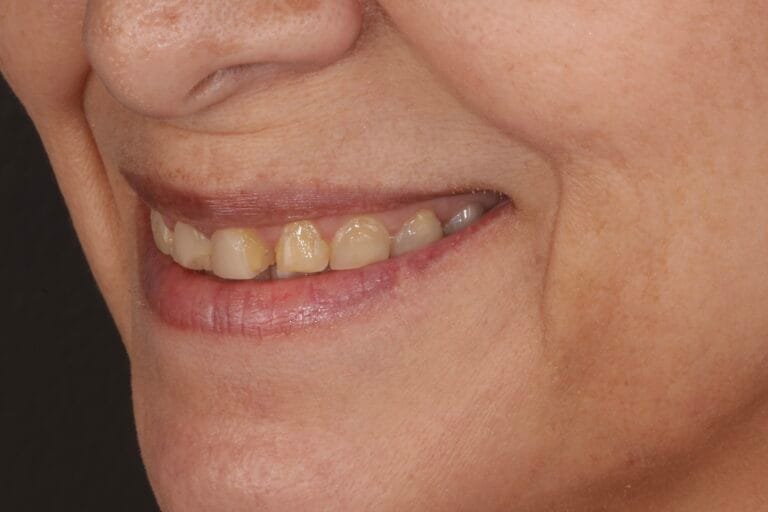
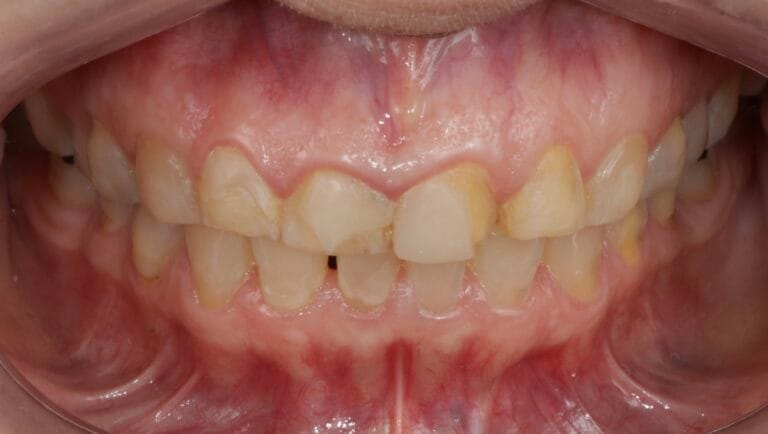
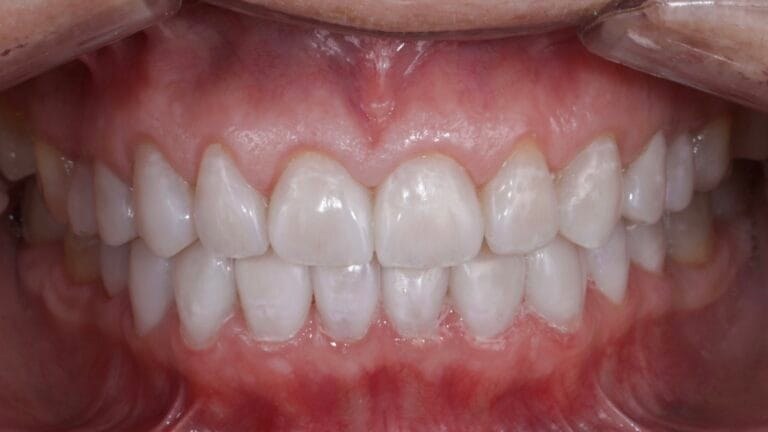
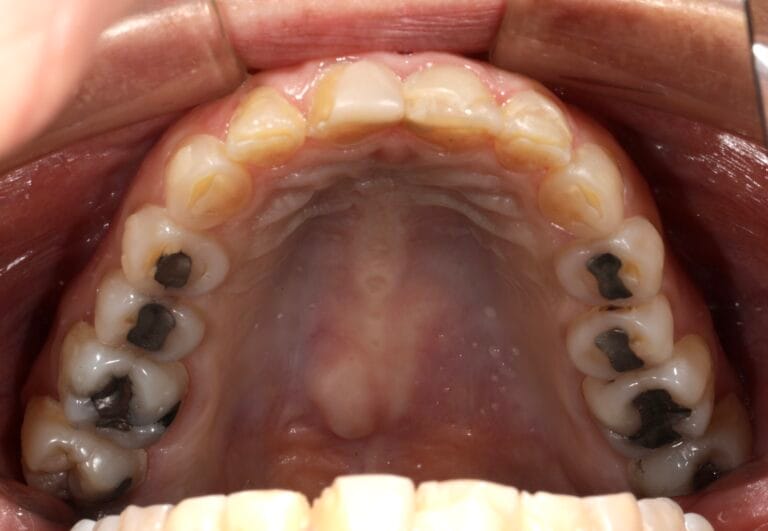
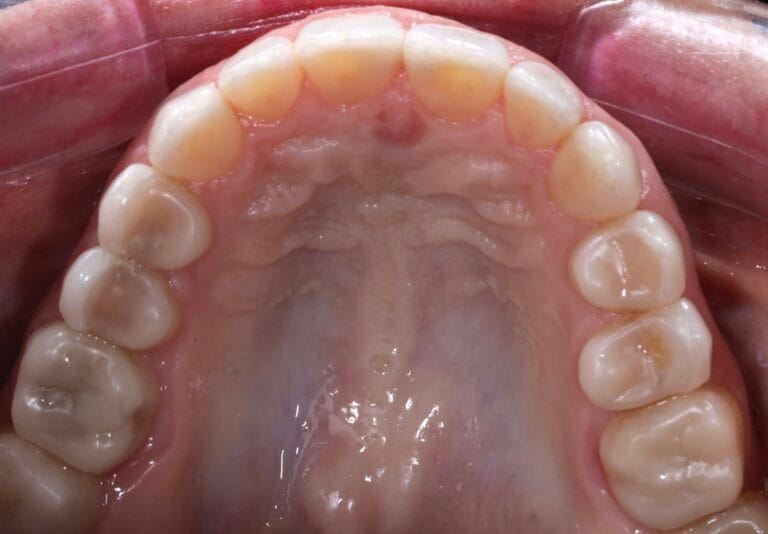
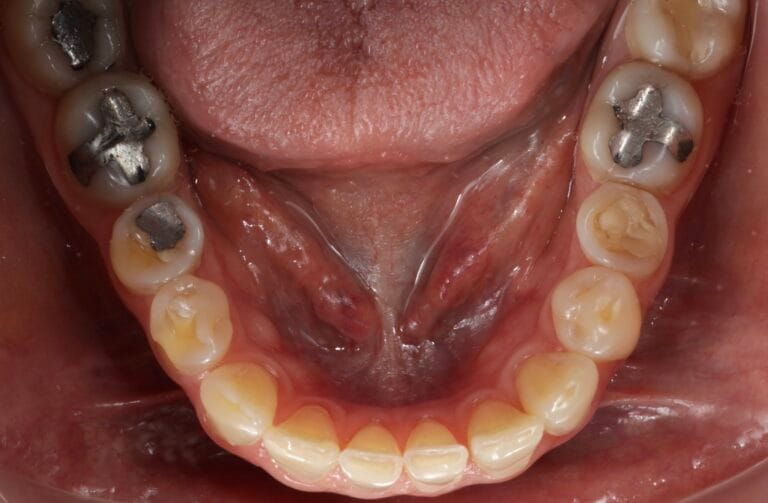
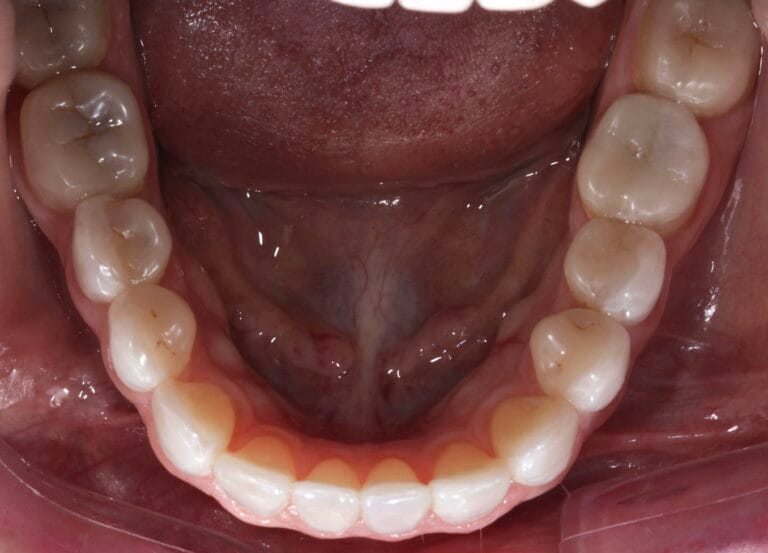
Figure 7. Intraoral photos before and after
TOOTH WEAR
Bruxism, characterized by involuntary rhythmic contractions of the masseter muscles and excessive teeth grinding, is a commonly overlooked yet significant condition. Symptoms can manifest during wakefulness or sleep and encompass primary and secondary forms. Sleep-related bruxism, associated with normal sleep arousals and various underlying medical conditions such as obstructive sleep apnea, Down syndrome, and medication effects, can cause considerable damage to teeth and dental work, resulting in morning jaw pain or fatigue, temporal headaches, and restricted motion of the temporomandibular joint. Although the diagnosis is primarily clinical, some patients with suspected sleep disorders such as obstructive sleep apnea require polysomnography. Clinicians utilize a comprehensive treatment approach encompassing counseling, lifestyle management, oral devices, and medication management to address bruxism.